Upgrading IoT Devices with Cellular Connectivity - Part 1

A New Approach to Connectivity for Medical Devices
Author: Manu Kemppainen, Bittium Fellow
Over the past years, the world of medical devices has been going through a major transition towards wireless connectivity. The goal is to provide new and more efficient ways to treat patients by providing wearable and wirelessly connected devices that can be used also outside the hospital.
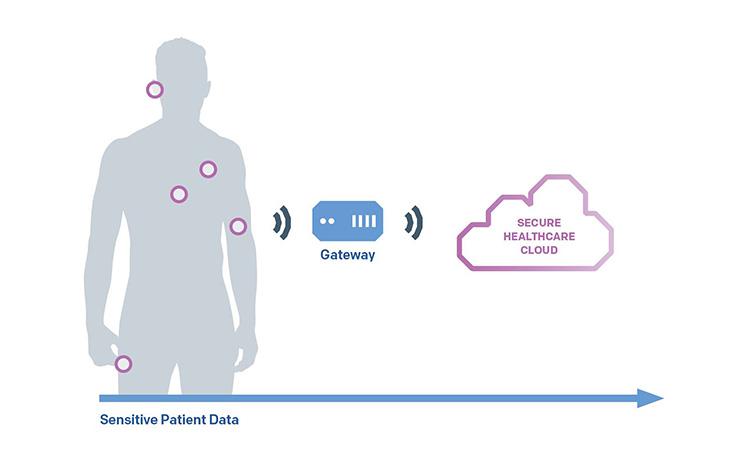
Many times, the solution is to provide local wireless connectivity for the devices, for example via Bluetooth to a separate gateway device. Even though this adds the wireless connectivity, it is often an additional step in transferring the patient data to a secure cloud or platform for data analyses.
Our R&D team has been a forerunner in the development of different wireless devices, including medical devices, and we saw that there could be a simpler way to reach the desired outcome. Based on this, we decided to do an in-depth analysis of the current situation with connected wearable medical devices and explore new approaches that could then be applied to wireless connectivity in any IoT solution.
Analysis: Where to Improve
One of the key items to analyze was the use of the wearable medical device together with the gateway device. The gateway device, which can be a smartphone for example, transmits the measured patient data to the medical cloud but can also bring along several disadvantages.
The combination of two devices can be an expensive solution for both the medical device provider as well as the treatment facility using it. Also, patients need to carry two different devices with them, and there is the need to charge both.
Both devices – the wearable medical device and the smartphone – need to be properly configured for the local connectivity (e.g., Bluetooth) between them to work. It was clear to us that this increases the administrative work and stress for the medical personnel, and consequently reduces the time for actual patient care.
The medical device and the phone always need to be in each other´s proximity, and finally, the smartphone needs to have cellular connection for the data transmission to the medical cloud to work.
The obvious conclusion was that if the medical device would include the cellular connectivity, we could get rid of the gateway device and the disadvantages it brings. The main question then was: How to best include cellular connectivity directly in the medical device?

Evaluating Key Elements for a New Approach
As with all device development, there were many elements and their interdependencies to take into consideration. Embedding connectivity to any device can be a challenge, but the small size required of wearable medical devices and other IoT devices, as well as the market specific requirements, demand specialized expertise. Especially the healthcare industry is one of the most regulated and strictly supervised markets for IoT devices and connected digital devices.
These were the main elements for evaluation:
- Device size
- Cellular network technology
- Modem evaluation
- Battery size and performance
- Temperature
- Antenna performance
- Software architecture
In addition to the evaluation the technical aspects of the device design, the following items needed to be analyzed and resolved before the device deployment:
- Live network performance
- Network monitoring
- Network subscription models
Continue to part 2 of the series!
Want to know more? Visit Bittium Cellular IoT Solution and Engineering Services for Industrial IoT and Medical & Healthcare
Manu Kemppainen, Bittium Fellow
Manu Kemppainen has over 30 years of experience in embedded software design and device development. He works as a Fellow at Bittium and has been with the company since 1999.
